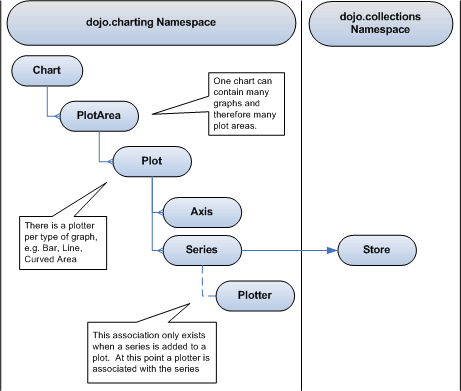
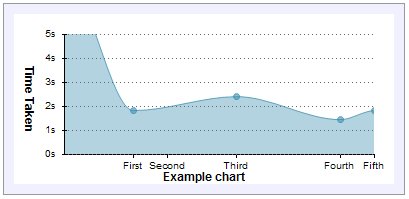
El ejemplo
Empecemos referenciando dojo y las librerias requeridas:
<script type="text/javascript" src="dojo/dojo.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
//Include the required dojo libraries/namespaces
dojo.require("dojo.collections.Store");
dojo.require("dojo.charting.Chart");
dojo.require('dojo.json');
</script>
Ahora definamos o recuperemos los datos con los que alimentaremos nuestra gráfica en una collection store. Se añaden a la gráfica como series, definidos asi:
var exampleData =
[
{ time: 10, count: 7382 },
{ time: 20, count: 1852 },
{ time: 35, count: 2397 },
{ time: 50, count: 1442 },
{ time: 55, count: 1854 }
];
var store = new dojo.collections.Store();
store.setData(exampleData);
var timeSeries = new dojo.charting.Series({
dataSource: store,
bindings: { x: "time", y: "count" },
label: "Example Series"
});
Ahora vayamos con la definiciones de los ejes donde podemos especificar el rango de display, el origen de datos y las etiquetas de los ticks de los ejes:
//Define the x-axis
var xAxis = new dojo.charting.Axis();
//Set the upper and lower data range values
xAxis.range = { lower: exampleData[0].time, upper: exampleData[exampleData.length-1].time };
xAxis.origin = "max";
xAxis.showTicks = true;
xAxis.label = "Example chart";
//Setup the x tick marks on the chart
xAxis.labels = [
{ label: 'First', value: 20 },
{ label: 'Second', value: 25 },
{ label: 'Third', value: 35 },
{ label: 'Fourth', value: 50 },
{ label: 'Fifth', value: 55 }
];
//Define the y-axis
var yAxis = new dojo.charting.Axis();
yAxis.range = { lower: 0, upper: 5000 };
yAxis.showLines = true;
yAxis.showTicks = true;
yAxis.label = "Time Taken";
//Setup the y tick marks on the chart
yAxis.labels = [
{ label: "0s", value: 0 },
{ label: "1s", value: 1000 },
{ label: "2s", value: 2000 },
{ label: "3s", value: 3000 },
{ label: "4s", value: 4000 },
{ label: "5s", value: 5000 }
];
Entonces definimos comos los datos serán mostrados definiendo el objeto Plot y asignandole las series con un pletter para pintarlas:
var chartPlot = new dojo.charting.Plot(xAxis, yAxis);
chartPlot.addSeries({
data: timeSeries,
plotter: dojo.charting.Plotters.CurvedArea
});
var chartPlotArea = new dojo.charting.PlotArea();
chartPlotArea.size = { width: 380, height: 170 };
chartPlotArea.padding = { top: 20, right: 20, bottom: 30, left: 50 };
//Add the plot to the area
chartPlotArea.plots.push(chartPlot);
var chart = new dojo.charting.Chart(null, "Example chart", "This is the example chart description");
//Add the plot area at an offset of 10 pixels from the top left
chart.addPlotArea({ x: 10, y: 10, plotArea: chartPlotArea });
//Setup the chart to be added to the DOM on load
dojo.addOnLoad(function()
{
chart.node = dojo.byId("GraphContainerArea");
chart.render();
});